I.Introduction
The regulations define three basic functions for switchgear in the design of an electrical installation.
1. Sectioning function
The purpose of disconnectors is to visibly open an electrical installation without loads at any point.
2. Command function
There are two types of command: Functional command and Safety command.
- Functional control (normal service) ensures the “ON” or “OFF” setting of an electrical system.
- The safety control (emergency stop) switches an electrical system “OFF” in the event of a danger to property or people.
3. Protection function
It makes it possible to limit the destructive or dangerous consequences of overcurrents or insulation faults and to separate the defective part from the rest of the installation.
The protective device must permanently leave the rated current (In), as well as normal overcurrents. It must carry out the safety cut-off and participate in the protection of people against indirect contact.
II. Sectioning devices
1. Disconnector
It is a device that makes it possible to separate (insulate) a live part upstream from a part downstream of an electrical circuit. The circuit is isolated off-load by opening all the line conductors (but not the PE conductor). The disconnector does not have breaking and closing powers. Locking is done by a padlock.
1.1. Fuse holder disconnector
It isolates and protects the live upstream part from the downstream part of an electrical circuit.
Criteria for choosing a fuse holder disconnector:
- Caliber and go.
- Protection class and operating voltage,
- Number of poles.
1.2. Isolator switch
It is used to manually separate and interrupt (open or close) a circuit under load. It has a breaking capacity.
Choice of switch disconnector
- Operating current and voltage,
- Breaking capacity: Breaking current.
- Number of poles (tripolar, bipolar, etc.).
III. protective devices
Protection devices trip in the event of anomalies (overloads, overcurrent, etc.).
Features:
- Operating current: Iu,
- Rated Current:In,
- Overcurrent: Motor start,
- Overload: Thermal overheating,
- Breaking capacity: Maximum current that a protective device can break a Pdc circuit (kA)
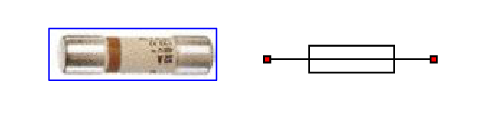
1. The fuse
It protects an electrical circuit against short circuits by melting the active part of the fuse. It includes a silica beam to quickly smother the electric arc and ensure insulation after the cut. There are several types of fuse.
Types:
gG cartridges (industrial use) protect electrical circuits against weak and strong overloads and against short circuits.
aM (Motor Accompaniment) cartridges protect electrical circuits against heavy overloads and short circuits.
UR (Ultra Rapid) cartridges protect electronic components.
2.Relay
It is a protective device that protects electrical circuits against overloads, short circuits or both. There are several types of triggers.
IV. Control and protection devices
1. Magnetic contactorµIt allows remote control of an electrical circuit under load, by current pulses (PB) and it is characterized by:
- Nominal voltage and current (In, Un),
- Ambient temperature and conventional thermal current (Ith)
Criteria for choosing a contactor:
- Number of poles
- Rated current and voltage
- Type of contactor coil power supply (220VAC; 24VDC)
- Lifetime.
2. Discontactor
It is equipped with a contactor plus a trip device, there are several types of circuit breakers: (thermal, magnetic and magnetothermal) and unipolar, bipolar and tripolar.
2. Discontactor
It is equipped with a contactor plus a trip device, there are several types of circuit breakers: (thermal, magnetic and magnetothermal) and unipolar, bipolar and tripolar.
Tags:
Electrical Installation
electrical maintenance
Electrical Preventive Maintenance
Electrical Wiring